How Leading Pharma Companies Achieve Digital Transformation in 2025
 Digital transformation is revolutionizing pharmaceutical development timelines that traditionally span over 10 years and cost billions of dollars. Nearly 85% of pharmaceutical companies have begun this digital experience, while 90% of organizations across industries undergo some form of digital transformation.
Digital transformation is revolutionizing pharmaceutical development timelines that traditionally span over 10 years and cost billions of dollars. Nearly 85% of pharmaceutical companies have begun this digital experience, while 90% of organizations across industries undergo some form of digital transformation.
Digitally mature pharma companies show impressive results. They reduce development timelines by up to 30% and improve patient outcomes by incorporating real-life data and digital biomarkers into trial design. Moderna’s digital-first approach produced remarkable results, moving from genetic sequence to vaccine in just 42 days. Pfizer achieved similar success by using AWS analytics and AI to cut clinical data processing from months to hours. One pharmaceutical manufacturer’s success story stands out – they upskilled 3,000 employees and achieved a 56% increase in labor productivity while reducing new product development lead times by 67%.
A new era unfolds in pharma as digital transformation increases efficiency, reduces timelines, optimizes resource allocation, and improves patient outcomes. Artificial intelligence, big data analytics, cloud computing, and blockchain power this transformation. This piece explores how leading pharmaceutical companies implement these technologies to achieve remarkable results in 2025.
Cloud-Native Platforms and AI for Accelerated Drug Discovery
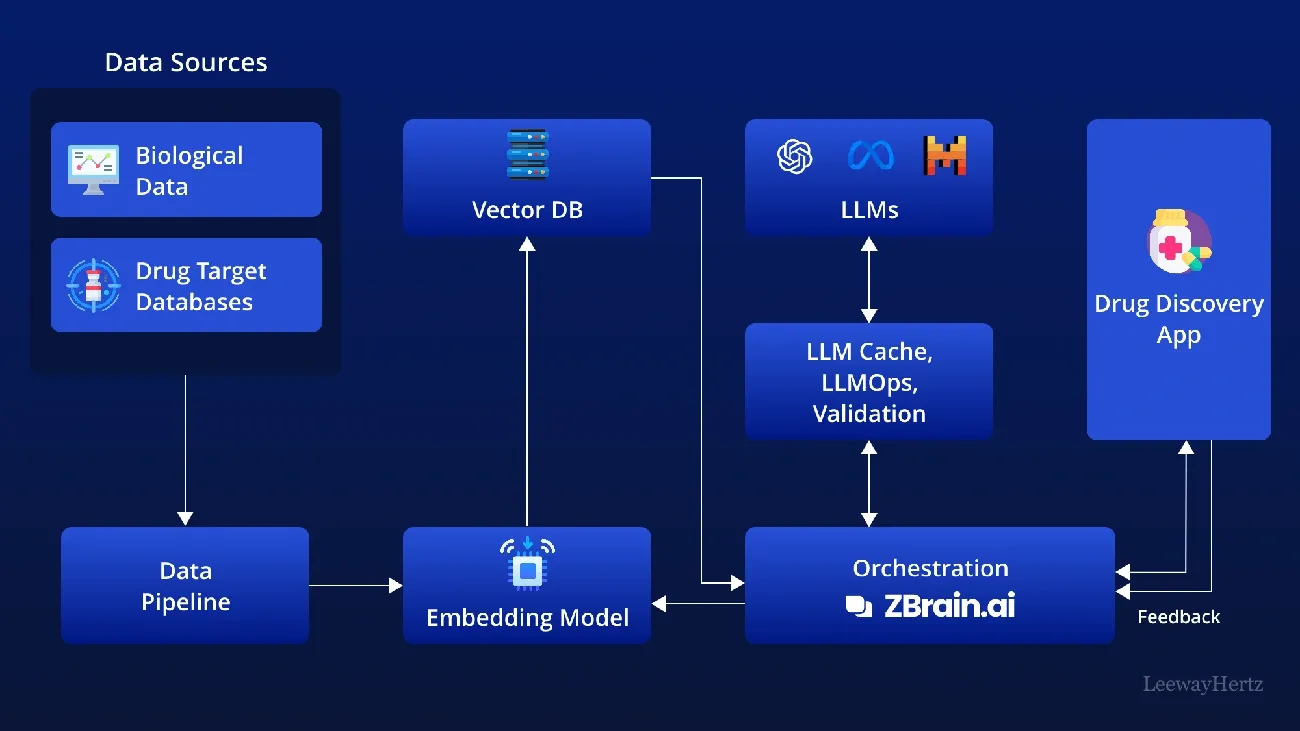
Image Source: LeewayHertz
Pharmaceutical companies now use cloud-native platforms and AI technologies to cut drug discovery timelines from years to months. The combination of advanced computing power with artificial intelligence marks a radical change in new treatment development.
Real-time compound modeling using AWS and Azure
Cloud platforms from Amazon and Microsoft provide the computational power needed for complex molecular simulations that once took months. Computational chemistry solutions like Promethium on AWS perform up to 100 times faster than traditional high-accuracy methods. This speed boost lets researchers analyze extensive datasets and molecular structures faster than conventional approaches. The result is a 50% reduction in drug discovery time.
Bayer’s work with Google Cloud shows how TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) scale up quantum chemistry calculations for early drug discovery. These specialized ML chips make possible the accurate in silico modeling of candidate drugs. AWS’s high-performance computing resources helped Schrödinger complete 16 million hours of GPU time (equivalent to 1,826 years of computing) in just months for COVID-19 antiviral discovery.
AI-guided candidate selection in early-stage R&D
AI systems transform how researchers identify promising drug candidates in early-stage research. AI creates novel drug molecules through molecular generation techniques. It predicts their properties and optimizes candidates through virtual screening.
Cloud-based AI platforms combine data, computational power, and algorithms to boost the success rates of drug research. Google Cloud’s Target and Lead Identification Suite predicts protein structure and function. Their Multiomics Suite integrates genomics data. Early adopters like Pfizer, Cerevel, and Colossal Biosciences can now predict protein 3D structures much faster.
Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine development pipeline
Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine development demonstrates technology’s role in emergency response acceleration. Their machine learning tool, Smart Data Query (SDQ), prepared clinical trial data for review in just 22 hours after meeting primary efficacy case counts. Demetris Zambas, Pfizer’s Vice President noted, “It saved us an entire month”.
The company expanded their clinical trial to 46,000 participants across 150 sites in six countries in just four months. Real-time predictive models of COVID-19 county-level attack rates helped select optimal clinical trial sites. Pfizer also deployed end-to-end cold chain capabilities with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and GPS tracking right after Emergency Use Authorization.
This digital transformation continues as Pfizer teams up with the Ignition AI Accelerator to create more efficient patient drafting systems and improve manufacturing processes. Their scientists now use Google’s cloud-based AlphaFold and machine learning models to assess target proteins and design new drug molecules quickly—work that once took months in the laboratory.
Advanced Analytics for R&D Optimization
Advanced analytics reshapes R&D decision-making in prominent pharmaceutical companies. This creates informed pathways that speed up drug development and make clinical trials better. Researchers now use artificial intelligence with big datasets to find promising targets and design more effective studies.
NAVIFY by Roche for oncology trial design
More than 18,000 oncology trials seek participants, yet less than 5% of cancer patients enroll in these studies. About 80% of trials fail to meet recruitment targets and timelines. Roche’s NAVIFY platform addresses this challenge through automated patient-specific trial screening. The system helps oncology care teams prepare, conduct, and document clinical treatment decisions by turning large amounts of data into useful information.
The NAVIFY Clinical Trial Match app finds trial options based on patient’s age, gender, biomarkers, and tumor information from 11 international registries. A groundbreaking large study with Ellis Fischel Cancer Center showed this digital solution standardizes tumor board workflow and saves time and money. Medical teams using NAVIFY report 20-30% better matching rates in trial enrollment.
AstraZeneca and BenevolentAI for kidney disease research
AstraZeneca started working with BenevolentAI in 2019 to speed up drug discovery for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Their partnership combines AstraZeneca’s genomics, chemistry, and clinical datasets with BenevolentAI’s target identification platform and biomedical knowledge graph.
The team has achieved early success – AstraZeneca picked their first AI-generated CKD target to move forward in drug development. Scientists from both companies work together. They use machine learning to analyze data and AI-based reasoning to infer previously unknown connections. This method proves especially valuable for complex diseases like CKD, which affects approximately 10% of the world’s population.
Centralized data lakes for hypothesis generation
Pharmaceutical companies now centralize R&D data using cloud-based platforms like data lakes or distributed data meshes. These systems aid efficient management of genomic and molecular information while meeting regulatory requirements.
Combined data and infrastructure layers allow analysis of multiple internal and external datasets. These include historical records, real-life evidence, external publications, and genome-wide association studies. Researchers can refine predictions, determine optimal experiments, and make better decisions about target selection through these analyzes.
Isolated data remains a challenge in pharmaceutical digital transformation. However, companies with advanced analytics capabilities have found working models that produce results. An advanced analytics capability could deliver “at least a 10 percent net impact from top- and bottom-line perspective,” according to Sai Jasti, GlaxoSmithKline’s chief data officer. This varies by product type and lifecycle stage.
Autonomous Labs and AI-Powered Molecule Screening

Image Source: SciTechDaily
Autonomous laboratories are changing how pharmaceutical research works. Machines now design, run, and modify experiments with minimal human oversight. These AI-driven systems bring unmatched speed and precision to drug discovery.
Insilico Medicine’s fibrosis candidate in 18 months
Insilico Medicine made a breakthrough with ISM001-055 (now called rentosertib). This AI-discovered small molecule for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) became the first to reach Phase II clinical trials. The company’s AI platform combined target identification, molecular generation, and synthetic route planning. The discovery process—from target identification to preclinical candidate selection—took just 18 months and cost under $2.60 million. Phase IIa results in 2025 showed the drug was safe, tolerable, and had good pharmacokinetics. Patients showed a 98mL improvement in lung function measured by FVC. The process worked 30 times faster than traditional methods. Each project needed only 60-200 molecules for testing instead of thousands used in conventional approaches.
GSK’s robotic lab for high-throughput screening
GSK has made automation central to their drug development process. The company sees it as key to streamlining processes and speeding up timelines. Their automated systems help spot bottlenecks and inefficiencies throughout the research pipeline. GSK scientists look at each step carefully when setting up new automated workflows. This includes data analysis, analytical sample testing, and workflow execution. The company now focuses on automated data reporting and user-friendly workflow consolidation. They also build advanced data pipelines with visualization tools to make better decisions.
Predictive analytics for compound efficacy
Machine learning algorithms have become powerful tools in drug discovery. They provide innovative ways to screen compounds virtually, identify targets, and optimize leads. These systems analyze patterns from clinical trials and ground evidence after collecting data. This helps predict how well drugs will work and how safe they’ll be. Predictive analytics proves valuable because it combines different types of data—clinical, biological, genomic, biomarker, and imaging information. AI-driven virtual screening looks at huge datasets of chemical compounds faster. It analyzes structural features, physicochemical properties, and molecular interactions to find compounds with the best therapeutic potential.
Wearables and Real-World Data for Personalized Trials
Wearable technology transforms clinical trials by enabling continuous patient monitoring beyond traditional healthcare settings. These devices capture vital data points that were previously impossible to measure in real-life conditions.
Novartis + Apple Health for cardiovascular monitoring
Novartis’s AWAKE-HF study utilizes wrist-worn digital accelerometers to track physical activity and sleep patterns in heart failure patients taking Entresto. The company’s collaboration with Tencent created an AI Nurse system within WeChat that alerts patients to signs of disease worsening. This system has identified 160,000 instances of potential heart failure deterioration since its 2020 launch. Biofourmis and Novartis have partnered on a digital therapeutic program that captures 22 different physiological parameters through upper-arm wearables.
Verily’s Project Baseline for adaptive trial design
Project Baseline’s community has grown to over 750,000 consented participants, with 2,500 enrolled in their landmark Health Study (2017-2023). The study combines extensive clinical assessments with continuous sensor monitoring via the Verily Study Watch. Each study visit provides participants with personalized results, and measurements like strength and balance are taken annually.
Digital biomarkers for early efficacy signals
Digital biomarker adoption in clinical trials has grown at a 34% annual rate (2000-2020). These technologies enable immediate detection of subtle neurological changes and facilitate early interventions vital for conditions from stroke to cognitive decline. Remote access makes clinical trials available to more diverse patient populations while reducing measurement bias.
IoT and Digital Twins in Smart Manufacturing
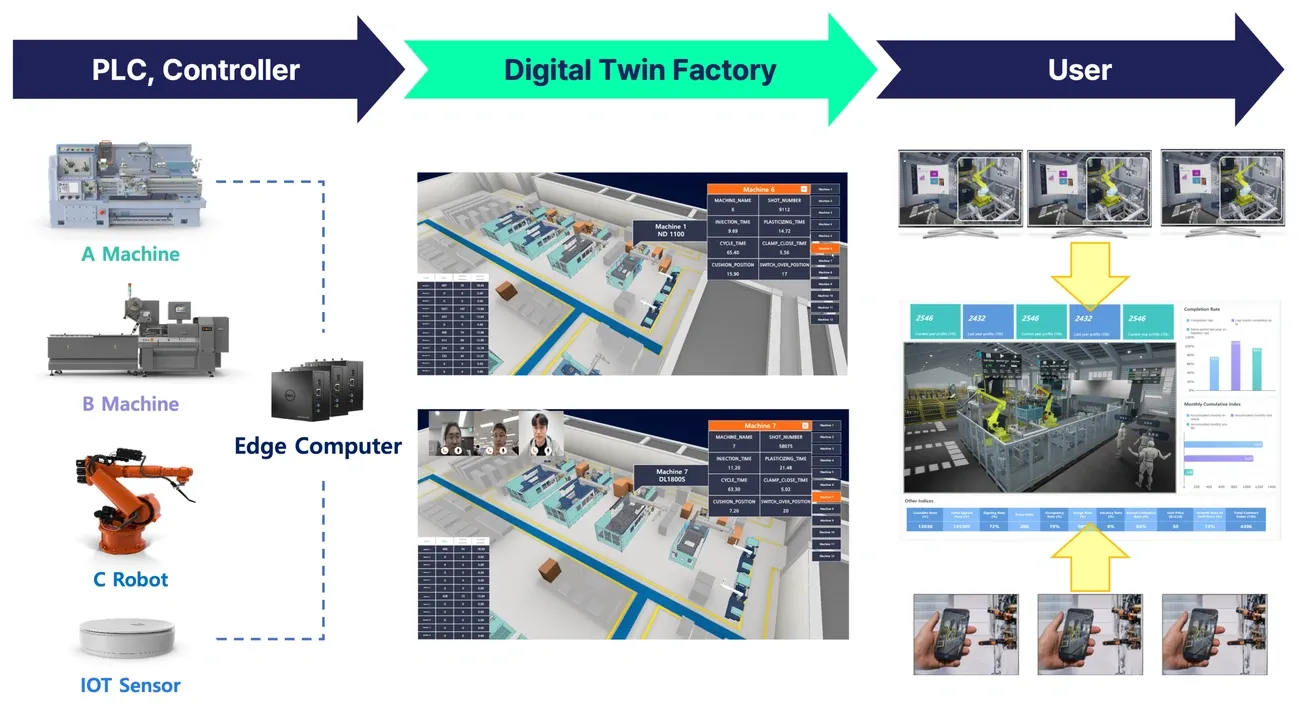
Image Source: MDPI
Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities have seen remarkable improvements thanks to Internet of Things (IoT) and digital twin technologies. These innovations allow companies to manage production with unprecedented precision, moving away from traditional reactive approaches.
Merck’s predictive maintenance with IoT sensors
Merck has rolled out predictive maintenance technology in its production facilities. The company uses sensors that gather process and machine data for immediate analysis. Their eight-year program targets rotating equipment like pumps, motors, and compressors. The centrifuges used to purify liquid crystals now have sensors that detect tiny vibrations and power supply changes that signal potential equipment failure. Working with Israeli startup Feelit, Merck uses nanotechnology sticker sensors to spot structural changes in mechanical systems before problems occur.
Novartis’ digital twin for process simulation
Novartis teamed up with AWS to create ‘Insight Centers’ that give operators worldwide interactive operational information. Their digital twins are virtual copies of physical processes that get continuous data from historians and IoT Greengrass edge devices. The system helped Novartis significantly reduce its process optimization time. Operators can now see dynamic views of global manufacturing processes in ways that weren’t possible before.
Real-time monitoring of environmental variables
IoT sensors do more than monitor equipment – they track crucial environmental factors like humidity, temperature, and pressure. PharmaWatch analyzes these variables and logs readings automatically in audit-ready formats, eliminating clipboards and manual work. The systems connect directly with OEMs to monitor chamber conditions without affecting internal environments.
Mobile Apps and Connected Devices for Patient Engagement

Image Source: Mobisoft Infotech
Mobile applications and connected devices are the life-blood of pharmaceutical digital transformation. These tools deliver measurable health improvements through up-to-the-minute monitoring and tailored support.
Roche’s MySugr app for diabetes management
Roche’s mySugr app was created by and for people with diabetes. The app serves over 6 million registered users worldwide and maintains a 4.6-star rating. This digital solution logs blood sugar readings automatically from connected meters. It also has features like bolus calculation, meal photo tracking, and detailed reporting. The results are remarkable. A retrospective analysis of Type 1 diabetes users revealed their estimated HbA1c dropped from 9% to 7.8% in just one month. Users also saw a 17.4% reduction in low blood sugar events over six months.
Propeller Health’s smart inhalers for COPD
Propeller Health is reshaping respiratory care with sensors that attach to existing inhalers. These sensors track medication usage and location data. The technology boosts medication adherence by up to 58% and cuts rescue inhaler use by up to 78%. The results are even more striking – asthma-related emergency visits drop by up to 57% and hospitalizations decrease by 35%. Propeller Health’s platform has medication reminders, air quality forecasts, and in-app refills.
Remote monitoring to reduce trial dropouts
Clinical trials now use connected devices to monitor participants continuously without frequent on-site visits. These technologies make data collection automatic and reduce the burden on participants. They also help reach patients in a variety of populations. All the same, success depends on thoughtful design that works for all users to prevent socioeconomic biases in recruitment.
Pharma-Startup Collaborations for Digital Innovation
Mutually beneficial alliances between pharmaceutical giants and agile startups drive digital breakthroughs in the industry today. These partnerships combine pharma’s extensive resources with startup creativity to develop powerful digital health solutions.
Bayer’s G4A accelerator for digital health startups
Bayer’s G4A stands as the original pharmaceutical accelerator program that has supported over 150 digital health companies and generated more than 30 commercial collaborations worldwide. The program’s rigorous selection process evaluates promising ventures from hundreds of applicants. One cycle alone reviewed over 400 applications from 65+ countries. Two distinct collaboration tracks exist in the program – the Growth Track provides €100,000 funding plus coaching for early-stage startups, while the Advance Track supports larger commercial deals.
Pfizer’s investment in Sidekick Health
The partnership between Pfizer and Nordic digital therapeutics company SidekickHealth represents a multi-million dollar commitment worth over $8 million to improve patient wellbeing across Europe. The platform started with inflammatory bowel disease patients in Finland and grew to include rheumatoid arthritis, atopic dermatitis, and psoriatic arthritis. Patients can now manage their nutrition, exercise, sleep, stress, and medication adherence through this solution.
Co-development of digital therapeutics platforms
The success of co-development depends on understanding operational differences between pharma and digital therapeutics companies. Traditional pharmaceutical companies follow structured drug development processes, while digital health companies work in a more iterative way. Pharmaceutical companies now see digital therapeutics as complementary to conventional medications that fill gaps in patient care through tailored interventions.
Conclusion
The digital revolution has reshaped every aspect of drug development in the pharmaceutical industry. AI and cloud computing serve as the life-blood technologies that slash discovery timelines from years to months. These advanced analytics enable researchers to make data-driven decisions that optimize R&D investments and clinical trial designs.
Digital twins and IoT sensors have transformed manufacturing processes. Companies can now predict equipment failures before they occur and maintain precise environmental controls. This move toward predictive operations marks a substantial change from traditional reactive approaches.
Patient participation has seen dramatic progress. Connected devices and specialized mobile apps provide live health monitoring that improves medication adherence and reduces emergency hospital visits. These technologies generate valuable ground data that feeds back into research and creates a continuous improvement cycle.
The most successful pharmaceutical companies collaborate with agile startups to speed up innovation cycles. This strategic blend of 50-year-old industry resources with entrepreneurial creativity works especially when you have to develop next-generation digital health solutions.
These transformations affect way beyond the reach and influence of operational efficiencies. Drug development timelines have dropped by up to 30%, which substantially speeds up patient access to life-saving treatments. Clinical trials have become more inclusive and capture diverse patient populations through remote monitoring capabilities. So the resulting medications better serve broader demographic groups.
The pharmaceutical digital transformation will without doubt continue its rapid progress. Companies that maintain their technological momentum while delivering meaningful value to patients, providers, and healthcare systems worldwide will thrive.
Key Takeaways
Leading pharmaceutical companies are leveraging digital transformation to revolutionize drug development, achieving unprecedented speed and efficiency in bringing life-saving treatments to market.
• AI and cloud platforms reduce drug discovery timelines by up to 50%, with companies like Insilico Medicine developing fibrosis candidates in just 18 months versus traditional 10+ year cycles.
• Real-world data from wearables and IoT devices enables personalized clinical trials, improving patient engagement and reducing trial dropouts while capturing diverse populations remotely.
• Digital twins and predictive analytics in manufacturing prevent equipment failures before they occur, with companies like Merck achieving substantial reductions in downtime through IoT sensor monitoring.
• Strategic pharma-startup partnerships accelerate innovation cycles, as demonstrated by Bayer’s G4A accelerator supporting 150+ digital health companies and generating 30+ commercial collaborations.
• Connected patient engagement tools deliver measurable health outcomes, with Roche’s MySugr app reducing diabetic patients’ HbA1c from 9% to 7.8% in just one month.
The most successful pharmaceutical companies are those that integrate these digital technologies holistically across their entire value chain—from discovery through manufacturing to patient care—creating a competitive advantage that translates directly into faster, more effective treatments for patients worldwide.


